区块链技术可为工业企业带来巨大益处。它有助于提高复杂供应链的透明度,减少延期和采购限制对生产和盈利的影响。

BLOCKCHAIN HAS THE POTENTIAL TO OFFER EFFICIENCIES AND IMPROVEMENTS IN MANY OF THE FOLLOWING AREAS:
区块链有望在以下多个领域提供助力:
Supply-chain monitoring for greater transparency into complex supply chains where delays and sourcing constraints impact production and profitability供应链监控:有助于提高复杂供应链的透明度,减少延期和采购限制对生产和盈利的影响
Identity management for when it is important to know who is taking an action and what their credentials are, including attorneys, auditors, engineers and technicians
身份管理:以便及时了解行动者的身份和资质(例如律师、审计师、工程师和技术人员)
Asset tracking to monitor equipment movements or intermodal logistics across carriers
资产跟踪:监控设备转移或跨承运商的多式联运物流
Quality assurance that can look across a production life cycle to gauge qualifications, quality, patterns of defects, etc.
品质保证:贯穿整个制造生命周期,评估资质、品质、缺陷等
Engineering design for long- duration, high-complexity products, for which delays in sharing updated engineering specifications or parts can increase rework and delay final delivery.
针对工期长、复杂度高的产品进行工程设计:避免因工程规格或配件更新不及时导致的返工和延期交付
Regulatory compliance enhanced by indelible records of actions taken, assets’ movements evidenced by permissioned consensus.
合规管理:通过不可磨灭的行动记录、经共识证明的资产转移来提高合规性
Materials provenance and counterfeit detection to reduce the $4.2 trillion impact of counterfeiting and piracy on the global economy by 2022, as cited by World Trademark Review
材料来源和假冒检测:根据《世界商标评论》的数据,截至2022年,假冒盗版造成的全球经济损失高达4.2万亿美元
Blockchain-powered solutions can bring together all of this information, delivering significant value for industrial companies, and can also help unlock the full potential of other advanced technologies like augmented reality, Internet of Things (IoT) and 3D printing
区块链驱动的解决方案,可整合所有信息,助力释放增强现实、物联网(IoT)和3D打印等先进技术的全部潜力,为工业企业带来巨大价值
Smart contracts
智能合约
Many of these functions can be automated through smart contracts, in which lines of computer code use data from the blockchain to verify when contractual obligations have been met and payments can be issued. Smart contracts can be programmed to assess the status of a transaction and automatically take actions such as releasing a payment, recording ledger entries, and flagging exceptions in need of manual intervention.
借助智能合约,许多职能都可实现自动化。智能合约利用计算机代码来读取区块链中的数据,验证何时履行了合同义务、何时可以付款。智能合约支持编程,可用于评估交易状态并自动采取行动,如放款、记录分类账条目以及标记需要人工干预的异常情况。
Traceability
可追溯性
If a company discovers a faulty product, the blockchain enables the firm and its supply chain partners to trace the product, identify all suppliers involved with it, identify production and shipment batches associated with it, and efficiently recall it.
如果发现产品有问题,企业及其供应链合作伙伴可借助区块链来追溯产品,找到与之相关的所有供应商、定位生产和装运批次并高效召回产品。
Accounts payable
应付账款
Blockchain can improve accuracy and efficiency in accounts payable management, an elaborate process that involves invoicing, reconciling invoices against purchase orders, keeping track of terms and payments, and conducting reviews and approvals at each step. Even though Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems have increased automation in these areas in recent years considerable manual intervention is still needed. And since neither of the transacting firms has complete information, conflicts often arise.
区块链可使应付账款管理工作更准确、更高效。应付账款管理十分复杂,需要开具发票、根据采购订单核对发票、跟进条款和付款,以及在各步骤审核批准。近年来,随着企业资源计划(ERP)系统的普及,上述流程的自动化程度有所提高,但仍需大量的人工干预。由于系统中交易双方的信息均不完整,因此常常会报错。
Cross-border trade
跨境贸易
Cross-border trade involves manual processes, physical documents, many intermediaries, and multiple checks and verifications at ports of entry and exit. Transactions are slow, costly, and plagued by low visibility into the status of shipments. Blockchain can increase transparency, verification and speed of processing throughout the chain of events.
跨境贸易涉及人工流程、实体单据、众多中间商以及出入境口岸的多重检验程序,具有速度慢、成本高、货物状态可视性低的缺点。区块链可以提高整个事件链的透明度,加快验证和处理速度。
DEFINING BLOCKCHAIN
区块链的定义
Blockchain is best known as the secure digital system behind bitcoin, the digital currency that operates independently of a central bank. Blockchain works as a distributed, or decentralised ledger, a digital system that records transactions among multiple parties in a verifiable, tamperproof way. Rather than being held in a single, centralised location, the blockchain is held by all the users in a network. While its use outside the finance world is still in the exploratory and developmental stages, manufacturing players are recognising that many elements of blockchain may be integrated into their operations to improve efficiency, security and transparency. To understand why this is, let’s look more closely as how a blockchain works.区块链最为人熟知的应用是作为比特币(一种独立于中央银行运行的数字货币)背后的安全数字系统。区块链是一种去中心化的分布式账本数字系统,以可验证、不可篡改的方式记录多方交易。区块链不集中保存在单一位置,而是由网络中的所有用户共同保存。虽然在金融领域之外,区块链的应用仍处于摸索阶段,但制造企业渐渐意识到,或许能借助区块链来提高运营的效率、安全性和透明度。为理解这背后的原因,我们不妨深入了解一下区块链的运作原理。
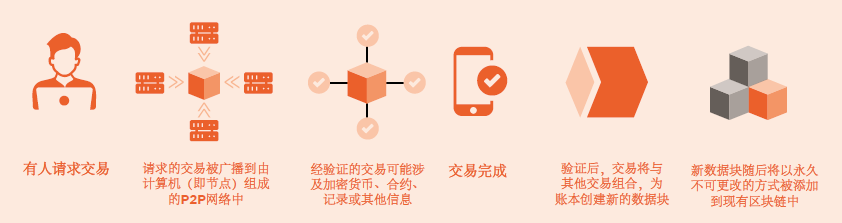
How blockchain works
区块链的运作原理
In general, all the users in the network, also known as network nodes, have copies of the same ledger. Transactions on a blockchain do not have to be financial—they simply represent a change in state for whichever data point the blockchain’s stakeholders want to track. A blockchain is valuable partly because it comprises a chronological string of blocks integrating all three types of activities in a supply chain: information, inventory and financial, capturing details that are not recorded in a traditional financial-ledger system. Moreover, each block is encrypted and distributed to all participants, who maintain their own copies of the blockchain. Thanks to these features, the blockchain provides a complete, trustworthy, and tamperproof audit trail. When blockchain record keeping is used, assets such as units of inventory, orders, loans, and bills of lading are given unique identifiers, which serve as digital tokens. Additionally, participants in the blockchain are given unique identifiers, or digital signatures, which they use to sign the blocks they add to the blockchain. Every step of the transaction is then recorded on the blockchain as a transfer of the corresponding token from one participant to another. Since participants have their own individual copies of the blockchain, each party can review the status of a transaction, identify errors, and hold counterparties responsible for their actions. No participant can overwrite past data because doing so would entail having to rewrite all subsequent blocks on all shared copies of the blockchain.
首先,网络中的所有用户,即网络节点,都拥有同一账本的副本。区块链上的交易不一定是财务交易,它们代表的是区块链利益相关者想要追踪的数据点的状态变化。区块链的价值在于,它由一串按时间顺序排列的区块组成,这些区块整合了供应链中所有三种类型的活动:信息、库存和财务,能够捕捉传统财务账本系统中未记录的细节。此外,每个区块都经过加密并分发给所有参与者,由他们维护各自的区块链副本。因此,区块链中的审计跟踪完整、可信且不可篡改。使用区块链保存记录时,库存量、订单、贷款、提货单等资产都被赋予唯一标识符,即数字代币。此外,区块链参与者在签署自己添加到区块链中的区块时,也需要使用自己的唯一标识符或数字签名。交易的每一步都记录在区块链上,体现为相应代币在参与者之间的转移。由于参与者拥有各自的区块链副本,因此每一方都可以查看交易状态、识别错误并要求交易方对自身行为负责。要修改数据就必须重写区块链所有共享副本上的每个后续区块,因此任何参与者都无法篡改历史数据。
How can blockchain in industry work in practice?
区块链如何应用于工业领域?
Simple blockchains can work well internally for a large manufacturer, by coordinating across its multiple internal ERP systems. When setting up a blockchain to manage supply chains with external partners, the partner companies have to take into consideration the security of their own data. One solution would be for the companies in question to agree to centralize their data on production and inventory-allocation decisions in a common repository. But this would require a huge level of integration. All involved companies would have to trust the others with their data and accept centralized decisions, regardless of whether they are partners or competitors, a solution that few would accept.
简易区块链有助于大型制造商统筹多个内部ERP系统。利用区块链来管理与外部合作伙伴的供应链时,合作伙伴必然会考虑自身数据的安全性。一种解决方案是,企业同意将其生产和库存决策的数据上传至共同数据库。但这需要大量整合工作,所有参与企业都必须信任其他企业提供的数据,并且无论是合作伙伴还是竞争对手,都必须接受集权决策。
A more practical solution is for participating companies to share their inventory flows on a blockchain and allow each company to make its own decisions, using common, complete information.
另一种更实际的解决方案是,参与企业在区块链上共享其库存流,并允许其他企业综合所有共享完整信息自行决策。
Part of the appeal of using blockchain to enhance supply chain efficiency and speed is that these applications, much like those for improving traceability, require participating companies to share only limited data—in this case, just inventory or shipment data.
利用区块链提高可追溯性时,参与方只需共享有限的数据。借助区块链提升供应链效率和速度的一大好处在于,参与方只需共享有限的库存或运输数据。


Limitations, dangers and solutions when using blockchain
区块链的局限性、风险及解决方案
It lacks speed for storage and retrieval存储和检索速度欠缺
It’s important to note that the encrypted linked list or chainlike data structure of a blockchain is not suited for fast storage and retrieval—or even efficient storage. And each link in the chain requires approval from all network partners before the step can be completed.
值得注意的是,区块链的加密链表或链式数据结构不支持快速存储和检索,甚至不支持高效存储。链中的每个环节都需经过网络中所有合作伙伴的批准才能完成。
So a blockchain would not replace the broad range of transaction-processing, accounting, and management-control functions performed by ERP systems, such as invoicing, payment, and reporting. Instead, the blockchain would interface with legacy systems across participating firms. Each firm would generate blocks of transactions from its internal ERP system and add them to the blockchain. This would make it easy to integrate various flows of transactions across firms.
因此,区块链无法代替ERP系统来执行开票、付款和报告等一系列交易处理、会计和管理控制职能,而是将与参与企业的传统系统对接。各企业将从内部ERP系统生成交易区块并添加到区块链中。由此,跨企业的交易流整合起来将更加容易。
Human error and malicious behaviour
人为错误和恶意行为
Even when a blockchain record is secure, there is still the danger that a contaminated or counterfeit product might be tagged and introduced into the supply chain, either in error or by a corrupt actor. Another danger is inaccurate inventory data resulting from mistakes in scanning, tagging, and data entry.
即使区块链记录的安全性很高,但仍存在一定风险,例如数据被污染或假冒产品被标记并引入供应链,可能是人为错误或恶意行为。另一大风险是由于扫描、标记和数据录入错误导致的库存数据不准确。
Companies are addressing these risks in three ways. First, they are stringently conducting physical audits when products first enter the supply chain to ensure that shipments match blockchain records. Second, they are building distributed applications, called dApps, that track products throughout the supply chain, check data integrity, and communicate with the blockchain to prevent errors and deception. If a counterfeit or an error is detected, it can be traced to its source using the blockchain trail of the transactions for that asset. Third, companies are making the blockchain more robust by using IoT devices and sensors to automatically scan products and add records to the blockchain without human intervention.
企业目前主要通过三种方式规避上述风险。首先,在产品初次进入供应链时进行严格的实物审核,确保货物与区块链记录相符。其次,构建去中心化应用程序,即dApp,在整个供应链中跟踪产品、检查数据完整性并与区块链通信,以防止错误和欺诈。一旦发现假冒产品或人为错误,可通过区块链上的资产交易记录追溯其来源。第三,使用物联网设备和传感器自动扫描产品并向区块链添加记录,无需人工干预。
Best practices for blockchain solutions
区块链解决方案的最佳实践
Blockchain solutions can create value for industrial companies in all the ways discussed above. But that does not mean that is the right solution for all companies and industrial manufacturing sectors. By focusing on four key areas early in their blockchain efforts, companies can set themselves on a path toward successful execution.
如上所述,区块链解决方案可以为工业企业创造价值,但这并不意味着它适用于所有企业和工业制造部门。企业在区块链搭建的早期阶段应关注以下四个关键领域,以便成功从中获益。
Make the business case
因案制宜
Blockchain needs to be a strategic fit. When there’s a need for different parties to share and update data, when time is of the essence and trust between parties is needed but intermediaries add too much complexity, then blockchain-based solutions can be very effective. But if none or only one or two of those types of challenges are present, then other solutions may be better placed.
区块链需与战略相匹配。当各方需要快速共享和更新数据,但彼此之间无法完全信任,且借助中介服务又太过繁琐时,基于区块链的解决方案就会非常有效。但是,如果不存在上述挑战,或只存在其中一到两个挑战,那么其他解决方案或许更适合。
Build an ecosystem
建立生态系统
Bringing together a group of stakeholders to collectively agree on a set of standards that will define the business model is perhaps the biggest challenge in blockchain. Participants have to decide the rules for participation, how to ensure that costs and benefits are fairly shared, what risk and control framework can be used to address the shared architecture, and what governance mechanisms are in place, including continuous auditing and validation, to ensure that the blockchain functions as designed.
企业应用区块链时面临的最大挑战是商业模式标准的制定。为了确保区块链按预期运作,所有利益相关者必须共同商定参与规则、公平的成本和收益分配原则、可用于共享架构的风险与控制框架、包括持续审计和验证在内的治理机制。
Design deliberately
精心设计
Much consideration must be given to a blockchain’s design. Will it be permissionless, allowing anyone to initiate and view transactions, or permissioned, restricting access to certain parties? No matter which model is chosen, it’s important to include cybersecurity, compliance, audit and legal specialists in important design decisions from the beginning.
区块链的设计必须经过深思熟虑。区块链应设置为允许所有人发起和查看交易,还是只允许具有权限的用户访问?无论选择哪种模式,都必须从一开始就由网络安全、合规、审计和法律专家共同参与关键设计决策。
Navigate and seek to shape regulatory uncertainty
驾驭并消除监管的不确定性
Regulators, elected officials and industry groups around the world are still evaluating potential responses to the increasing prevalence of blockchain enabled solutions. It is important to engage with these players, to make the case that blockchain technology can be trusted. Blockchain’s potential for transparency, as well as the immutable record it creates, could make it a powerful tool for regulators.
随着区块链解决方案日益普及,世界各地的监管机构、政府官员和行业团体仍在评估其潜在影响。一旦上述各方充分了解区块链技术,便会发现其可信度很高。区块链上的记录透明度高且不可篡改,有望成为有力的监管工具。
Conclusions
结语
As blockchain is integrated more and more into the factories and supply chains of the future, the improvements in speed of processes, accuracy and traceability of data, quality control and security all have the potential to impact on staff levels and working practices. While automation, aided by blockchain, may reduce the necessity for worker numbers in certain roles, the need for highly skilled staff to manage the digitised processes will increase. Additionally, in many cases, blockchain is an aid to efficiency, not a replacement for necessary human intervention, which will be required in the foreseeable future for tasks such as auditing and essential communication between partners.
未来,随着区块链在工厂和供应链中的普及,流程速度、数据准确性与可追溯性、品质控制与安全性将得以提升,这可能会对工作岗位和工作实践产生影响。在区块链的作用下,自动化水平会提高,某些岗位的人员需求会相应减少,但针对管理数字化流程的高技能员工的需求将增加。此外,在许多情况下,区块链的应用旨在提高效率,而非替代必要的人工干预。在可预见的未来,审计、合作伙伴间的重要沟通等任务仍然离不开人工干预。

版权归广东奥马冰箱有限公司所有,转载请注明出处。